The ability to organize and prioritize tasks are essential skills for holding a leadership position and generating good results.
The Eisenhower Matrix is a technique that allows you to put these skills into practice to define your priorities effectively and aid your decision-making.
Simple and effective, this tool can be used in the strategic planning of any company and even in the daily routines of professionals.
Check out our article to better understand what the Eisenhower Matrix is and how to apply it to your work or personal life.
What is the Eisenhower Matrix?
The Eisenhower Matrix is a time management technique that organizes tasks by their urgency and importance, allowing you to prioritize the most relevant work efficiently.
The matrix is composed of four quadrants:
- Important and urgent
- Important, but not urgent
- Not important, but urgent
- Not important and not urgent
The initial concepts for creating the technique were introduced by the 34th President of the United States, Dwight D. Eisenhower.
The method was created because he noticed that many people wasted a lot of time on activities that were urgent but not important.
In his view, people needed to focus on important tasks, even if they weren’t urgent.
In this context, the matrix became a useful tool for managing time and making better decisions.
However, it’s important to have good discernment to classify whether activities are important or urgent.
How to distinguish between important and urgent tasks using the Eisenhower Matrix?
Focusing on simplicity, the Eisenhower Matrix is an excellent methodology to aid in decision-making.
The method basically consists of classifying tasks into the four types we mentioned.
This way, it will be possible to define a structure to analyze your items and decide the priority of each one.
The first step to putting the technique into practice is to identify the category of your activities:
- Important and urgent: These are tasks that need to be done immediately and will have a significant impact on your goals.
- Important but not urgent: These are tasks that will contribute to your long-term goal, but do not need to be done immediately.
- Not important but urgent: These are tasks that need to be done as soon as possible, but do not contribute to your goals.
- Not important and not urgent: These are tasks that do not require attention.
After identifying the activities of your matrix, you will need to make decisions about how and when they will be carried out:
- Important and urgent tasks: these should be your highest priority, while non-urgent and unimportant tasks can be ignored.
- Important but not urgent tasks: these can be scheduled for later.
- Unimportant but urgent tasks: it’s important to deal with them as soon as possible to avoid negative consequences.
How are the four quadrants of the Eisenhower Matrix divided?
As we explained, the Eisenhower Matrix uses task division to understand which demands need to be prioritized, scheduled, and delegated.
See below a graphical representation of this method:
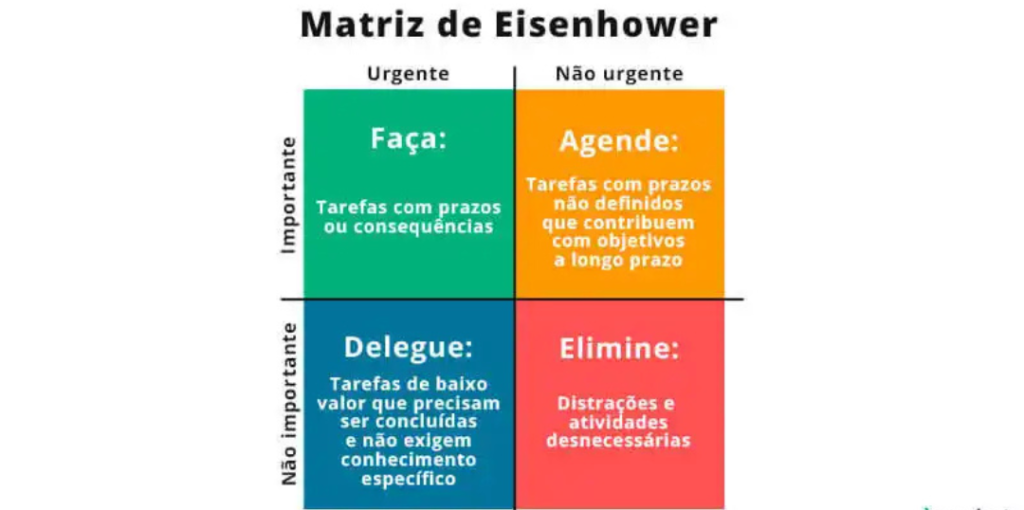
1st quadrant: do
This quadrant is reserved for tasks that require immediate action and have top priority.
There should be no doubt about which items fit here, as they are usually already a priority and require more attention.
2nd quadrant: schedule
Here are the tasks that are important but not urgent.
Items in this area need to be scheduled for later, as they will require your attention since they are linked to long-term goals.
Quadrant 3: Delegate
This quadrant includes tasks that are not critical but need to be completed urgently.
Items placed here usually arise suddenly and require immediate action.
It’s important to assess whether these tasks are not essential and do not require much time. If so, it will be possible to delegate the activities to someone else.
Quadrant 4: Eliminate
The items in this quadrant often can’t even be considered tasks.
Generally, this section contains distractions and unnecessary tasks that should be avoided and removed from your to-do list.
What are the advantages of applying the Eisenhower Matrix?
The main benefit of this time management technique is that it offers a clearer path to your goals.
Mapping and classifying activities helps you find the right direction and define priorities to achieve it.
In addition, there are several other advantages that applying the Eisenhower Matrix can generate:
- Simplifying decision-making: Visualizing tasks helps when making decisions, especially when choosing what needs to be done “now.”
- Efficient time management: Defining the priority of activities is a task in itself and not so simple. Applying the matrix is a smart way to prioritize the most important activities.
- Improved productivity: Applying the matrix correctly helps increase productivity by focusing on the most important tasks with an organized approach.
- Stress reduction: Optimizing time and decision-making helps reduce stress considerably.
- Focus on objectives: It helps identify what really matters for your goals, not just urgent activities that will be done to avoid consequences.
4 tips on how to prioritize tasks using the Eisenhower Matrix
Below are some tips to help you prioritize your activities within the matrix.
Use colors to identify tasks.
An interesting approach is to use a color code to better visualize high-priority items.
Here’s a suggested color system:
- Green: Top priority
- Orange: Secondary priority
- Blue: Tertiary priority
- Red: Not a priority
The idea is that each of these colors is applied to a quadrant, just like in our visual example.
Set a limit of 10 tasks per group.
Try to use a limited number of tasks in each quadrant of your matrix to ensure it remains well-organized and easy to understand.
Separating the items that will go into your matrix will also help in identifying priorities.
Create separate personal and professional to-do lists.
Separating personal and professional tasks is a way to limit the items that will go into your Eisenhower Matrix.
This is important to clearly differentiate personal goals from professional goals, allowing you to maintain focus on them at the right time.
Eliminate first, then prioritize.
Another way to optimize the organization of priorities is to eliminate unnecessary activities. The idea is to fill the fourth quadrant before the others.
This is important to save time when organizing and planning our work, allowing the focus to remain only on productive activities.
Ready to use the Eisenhower Matrix?
We hope our content has helped you understand what the Eisenhower Matrix is and how to create one for your professional or personal life.
If you’re looking for a practical digital way to create and track your matrix, check out MindMeister.
MindMeister is a mind mapping tool that offers a variety of resources and templates, including a ready-made Eisenhower Matrix template.

